Pagination in Django.
Display a huge list of content sliced on multiple pages with Pagination.
Pagination is the process of splitting the contents of a website, or a section of contents from a website, into discrete pages. One should use pagination to make his/her website more efficient to use when working with a huge list of contents for example "List of 100 blog posts". Also, paginating the content helps websites from being overcrowded with the content and makes visitors focus on small content at a time. This increases the readability and visitors are likely to return to your website again.
Django has a pre-built class called "Paginator" to create and manage the paginated data. It can be imported by the following code.
from django.core.paginator import Paginator
In Django, views are of two types which are Function-based views and Class-based views. Both types of views have different ways of paginating the content but the overall work is the same.
For this tutorial, we will be using my project called "One for all Blogging platform". For the full source code of my project visit the oneforall-blog GitHub repository.
In this project, I have created an app named blog which has the function-based view "HashnodeView" with the following code,
blog/views.py
def HashnodeView(request):
posts = get_hashnode_blogs()
return render(request, 'blog/news_posts.html',{'posts':posts})
The HashnodeView function collects data from another function and passes it to a template named hashnode_posts.html and then the template displays that data. The HTML code looks like this.
blog/template/blog/hashnode_posts.html
{% for post in posts %}
<div class="col">
....
<h5 class="mb-1">{{ post.title }}</h5>
....
</div>
{% endfor %}
Currently, the HashnodeView and the hashnode_posts.html template display all the items stored in the posts on a single page. That looks very crowded and lengthy. So we need to add some code to paginate these items.
Let's first import the Paginator using the following line of code.
from django.core.paginator import Paginator
In function-based views, we need to specify the data and the number of items by which we want to paginate this data. For the HashnodeView we want to paginate the contents of posts by 9 items. Also, in the previous code, we returned the posts to the template but now we will need to return paginated data that is page_obj. The final code will become,
Project directory: blog/views.py
from django.core.paginator import Paginator
def HashnodeView(request):
posts = get_hashnode_blogs(1)
paginator = Paginator(posts, 9)
page_number = request.GET.get('page')
page_obj = paginator.get_page(page_number)
return render(request, 'blog/hashnode_posts.html', {'page_obj': page_obj})
Now that we have paginated the data successfully we need to display it in our hashnode_posts.html template. Also, we have to add a navigation panel for the visitors to navigate between the pages. But not to worry, there are few lines of code to include simple navigation with the links for the first, previous, next and last page. So the final template will look like this,
Project directory: blog/template/blog/hashnode_posts.html
{% for posts in page_obj %}
<div class="col">
....
<h5 class="mb-1">{{ post.title }}</h5>
....
</div>
{% endfor %}
<!-- For page navigation links -->
<div class="pagination" style="width: fit-content;">
<span class="step-links">
{% if page_obj.has_previous %}
<a href="?page=1" class="page-link" style="display: inline;">« first</a>
<a href="?page={{ page_obj.previous_page_number }}" class="page-link" style="display: inline;">previous</a>
{% endif %}
<span class="current">
Page {{ page_obj.number }} of {{ page_obj.paginator.num_pages }}.
</span>
{% if page_obj.has_next %}
<a href="?page={{ page_obj.next_page_number }}" class="page-link" style="display: inline;">next</a>
<a href="?page={{ page_obj.paginator.num_pages }}" class="page-link" style="display: inline;">last »</a>
{% endif %}
</span>
</div>
And that's it. After running the server you will get nicely organised content with the navigation links to move between the pages.
| Before Pagination | After Pagination |
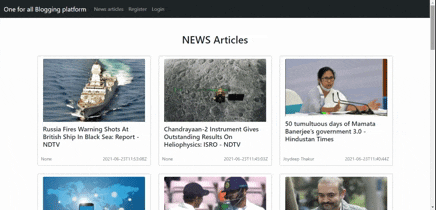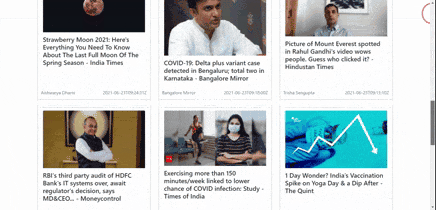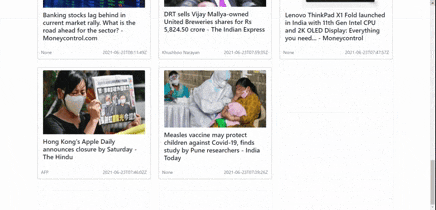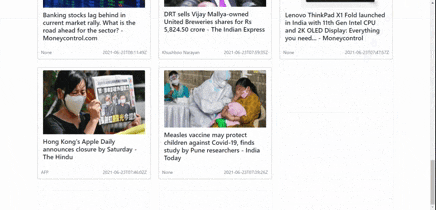 |  |
In the case of Class-based Listview, we don't need to import the Paginator as ListView has its own way of paginating the List. All we have to do is specify the number by which we want to paginate the list. The project "One for all Blogging system" also has a class-based view named HomeView which is paginated by 6 items.
Project directory: blog/views.py
from django.views.generic import ListView
class HomeView(ListView):
paginate_by = 6
model = Post
template_name = 'blog/home.html'
ordering = ['-post_date']
The remaining steps are the same as in the function-based view. We can add navigation links just like we did with our HashnodeView. You can see the code for template home.html here.
Visit the One for all Blogging platform at oneforall-blog.herokuapp.com to see the working of our code.
And that's all about the Pagination in Django. For the full source code of my project visit the GitHub repo here and give it a star if you like my work.
I hope this article was helpful for you. Please do subscribe to the newsletter to get my blog posts directly in your mailbox📬.